- What is Kubernetes?
- Why You Need Kubernetes and What It Can Do
- Key Features of Kubernetes
- Node Components
- Addons
- Understanding Kubernetes Architecture
- Practical Learning: Responsive Tutorials and Practical Experience
- Advanced Topics: Scaling Beyond the Basics
- Real-World Applications of Kubernetes
- Conclusion:
If you're new to Kubernetes, getting started can feel overwhelming. A solid introduction to Kubernetes goes beyond basic concepts—it requires hands-on practice, a deep understanding of the Kubernetes framework, and knowledge of real-world applications. In this guide, we’ll explore collaborative learning methods, advanced topics, and real-world cases to help you handle Kubernetes with confidence.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetesis an open-source container orchestration system used for automating computer application deployment, scaling, and management. In other words, you use Kubernetes to make serious magic with containers. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
The name Kubernetes originates from Greek, meaning helmsman or pilot. Google open-sourced the Kubernetes project in 2014. Kubernetes combinesover 15 years of Google's experiencerunning production workloads at scale with best-of-breed ideas and practices from the community.
Here’s how Dan Kohn, executive director of theCloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF),in a podcast with Gordon Haff, explained it: “Containerization is this trend that’s taking over the world to allow people to run all kinds of different applications in a variety of different environments. When they do that, they need an orchestration solution to keep track of all of those containers and schedule them and orchestrate them. Kubernetes is an increasingly popular way to do that.”
Why You Need Kubernetes and What It Can Do
Containers are a good way to bundle and run your applications. In a production environment, you need to manage the containers that run the applications and ensure that there is no downtime. For example, if a container goes down, another container needs to start. Wouldn't it be easier if this behavior was handled by a system?
That's how Kubernetes comes to the rescue! Kubernetes provides you with a framework to run distributed systems resiliently. It takes care of scaling and failover for your application, provides deployment patterns, and more. For example, Kubernetes can easily manage a canary deployment for your system.
Kubernetes provides you with:
- Service discovery and load balancingKubernetes can expose a container using the DNS name or using their IP address. If traffic to a container is high, Kubernetes can load balance and distribute the network traffic so that the deployment is stable.
- Storage orchestrationKubernetes allows you to automatically mount a storage system of your choice, such as local storage, public cloud providers, and more.
- Automated rollouts and rollbacksYou can describe the desired state for your deployed containers using Kubernetes, and it can change the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate. For example, you can automate Kubernetes to create new containers for your deployment, remove existing containers and adopt all their resources to the new container.
- Automatic bin packingYou provide Kubernetes with a cluster of nodes that it can use to run containerized tasks. You tell Kubernetes how much CPU and memory (RAM) each container needs. Kubernetes can fit containers onto your nodes to make the best use of your resources.
- Self-healingKubernetes restarts containers that fail, replaces containers, kills containers that don't respond to your user-defined health check, and doesn't advertise them to clients until they are ready to serve.
- Secret and configuration managementKubernetes lets you store and manage sensitive information, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and SSH keys. You can deploy and update secrets and application configuration without rebuilding your container images, and without exposing secrets in your stack configuration.
Kubernetes Components
When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster.
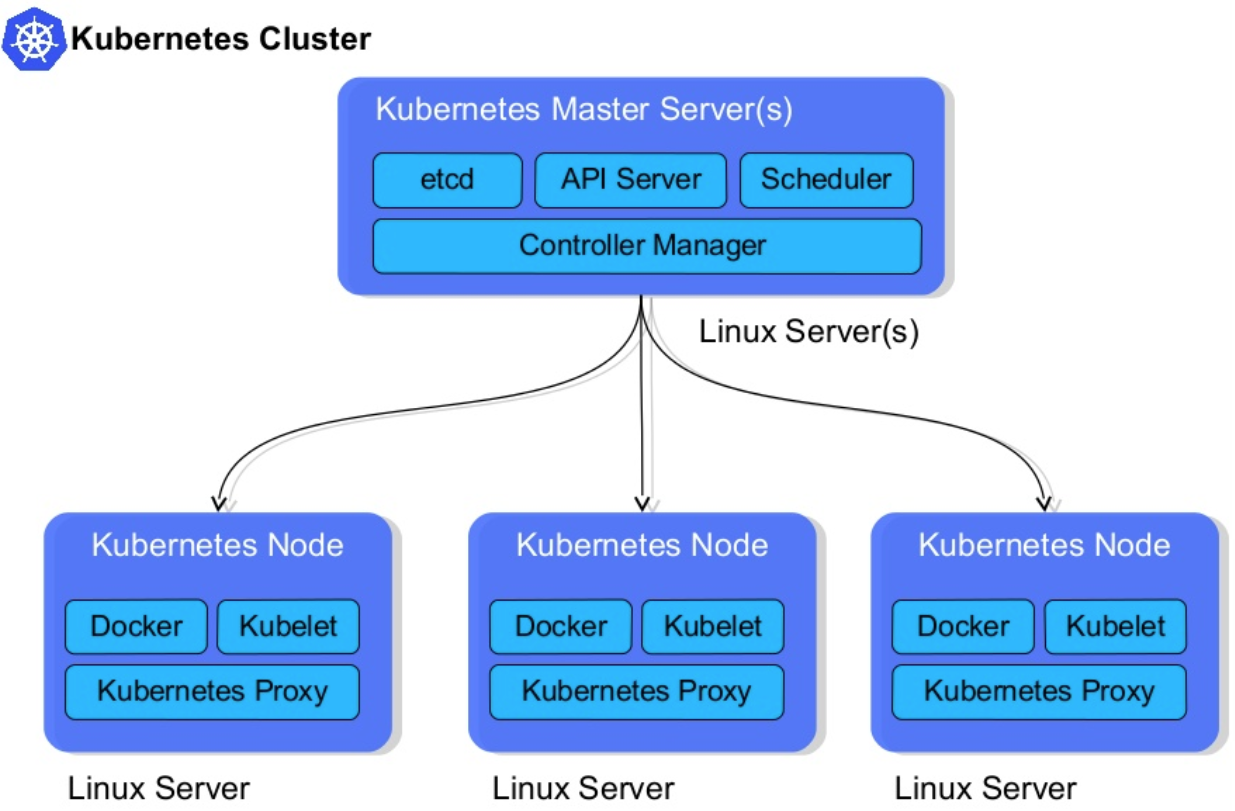
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of worker machines, callednodes, that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node.
The worker node(s) host thePodsthat are the components of the application workload. Thecontrol planemanages the worker nodes and the Pods in the cluster. In production environments, the control plane usually runs across multiple computers and a cluster usually runs multiple nodes, providing fault-tolerance and high availability.
Control Plane Components
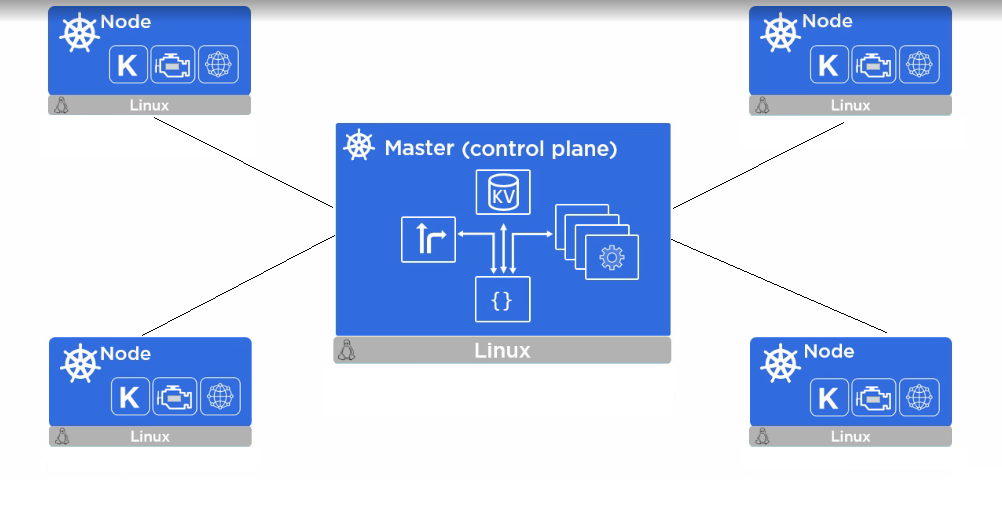
The control plane's components make global decisions about the cluster (for example, scheduling), as well as detecting and responding to cluster events (for example, starting up a newpodwhen a deployment's replicas field is unsatisfied).
Control plane components can be run on any machine in the cluster. However, for simplicity, set up scripts typically start all control plane components on the same machine, and do not run user containers on this machine.
kube-apiserver
The API server is a component of the Kubernetescontrol planethat exposes the Kubernetes API. The API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
The main implementation of a Kubernetes API server iskube-apiserver. kube-apiserver is designed to scale horizontally—that is, it scales by deploying more instances. You can run several instances of kube-apiserver and balance traffic between those instances.
etcd
Consistent and highly-available key-value store used as Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster data.
If your Kubernetes cluster uses etcd as its backing store, make sure you have abackupplan for those data.
kube-scheduler
Control plane component that watches for newly createdPodswith no assignednode, and selects a node for them to run on.
Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include individual and collective resource requirements, hardware/software/policy constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines.
kube-controller-manager
Control Plane component that runscontrollerprocesses.
Logically, eachcontrolleris a separate process, but to reduce complexity, they are all compiled into a single binary and run in a single process.
These controllers include:
- Node controller: Responsible for noticing and responding when nodes go down.
- Replication controller: Responsible for maintaining the correct number of pods for every replication controller object in the system.
- Endpoints controller: Populates the Endpoints object (that is, joins Services & Pods).
- Service Account & Token controllers: Create default accounts and API access tokens for new namespaces.
cloud-controller-manager
A Kubernetescontrol planecomponent that embeds cloud-specific control logic. The cloud controller manager lets you link your cluster into your cloud provider's API, and separates the components that interact with that cloud platform from components that just interact with your cluster.
The cloud-controller-manager only runs controllers that are specific to your cloud provider. If you are running Kubernetes on your premises, or in a learning environment inside your PC, the cluster does not have a cloud controller manager.
As with the kube-controller-manager, the cloud-controller-manager combines several logically independent control loops into a single binary that you run as a single process. You can scale horizontally (run more than one copy) to improve performance or to help tolerate failures.
The following controllers can have cloud provider dependencies:
- Node controller: For checking the cloud provider to determine if a node has been deleted in the cloud after it stops responding
- Route controller: For setting up routes in the underlying cloud infrastructure
- Service controller: For creating, updating, and deleting cloud provider load balancers
Key Features of Kubernetes
- Scalability:Kubernetes can scale without burdening your ops team.
- Flexibility:Kubernetes’ flexibility grows with you to deliver your applications consistently and easily no matter how complex your need is.
- Run Anywhere:Kubernetes is open source, giving you the freedom to take advantage of on-premises, hybrid or public cloud infrastructure, and letting you effortlessly move workloads to where they’re most needed.
- Automation:Automatically place containers based on their resource requirements and other constraints without sacrificing availability. Mix critical and best-effort workloads to drive utilization and save resources.
- Self-Healing:Restart containers that fail, replace and reschedule containers when nodes die. Kill containers that don't respond to your user-defined health check.
- Self-Discovery & Load Balancing:Kubernetes gives containers their own IP addresses and a single DNS (domain name server) name for a set of containers, and it can load-balance.
- Automated rollouts & rollbacks:Kubernetes progressively rolls out changes to your application or its configuration, while monitoring application health to ensure it doesn't kill all your instances at the same time. If something goes wrong, Kubernetes will roll-back the change for you.
- Batch Execution:Kubernetes can manage your batch and continuous integration (CI) workloads, replacing containers that fail, if desired.
Node Components
Node components run on every node, maintaining running pods and providing the Kubernetes runtime environment.
kubelet
An agent that runs on eachnodein the cluster. It makes sure thatcontainersare running in aPod.
The kubelet takes a set of PodSpecs that are provided through various mechanisms and ensures that the containers described in those PodSpecs are running and healthy. The kubelet doesn't manage containers that were not created by Kubernetes.
kube-proxy
kube-proxy is a network proxy that runs on eachnodein your cluster, implementing part of the KubernetesServiceconcept.
kube-proxymaintains network rules on nodes. These network rules allow network communication to your Pods from network sessions inside or outside of your cluster.
kube-proxy uses the operating system packet filtering layer if there is one and it's available. Otherwise, kube-proxy forwards the traffic itself.
Container runtime
The container runtime is the software that is responsible for running containers.
Kubernetes supports several container runtimes:Docker,containerd,CRI-O, and any implementation of theKubernetes CRI (Container Runtime Interface).
Addons
Addons use Kubernetes resources (DaemonSet,Deployment, etc) to implement cluster features. Because these are providing cluster-level features, namespaced resources for addons belong within the kube-system namespace.
Selected addons are described below.
DNS
While the other addons are not strictly required, all Kubernetes clusters should havecluster DNS, as many examples rely on it.
Cluster DNS is a DNS server, in addition to the other DNS server(s) in your environment, which serves DNS records for Kubernetes services.
Containers started by Kubernetes automatically include this DNS server in their DNS searches.
Web UI (Dashboard)
The dashboardis a general-purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage and troubleshoot applications running in the cluster, as well as the cluster itself.
Container Resource Monitoring
Container Resource Monitoringrecords generic time-series metrics about containers in a central database and provides a UI for browsing that data.
Cluster-level Logging
Acluster-level loggingmechanism is responsible for saving container logs to a central log store with a search/browsing interface.
Understanding Kubernetes Architecture
A strong foundation in the Kubernetes framework is important for effective cluster management. Kubernetes operates using a Kubernetes API, which serves as the central point of communication between users, cluster components, and external tools.
The core components include:
- Control Plane – Manages cluster operations, scheduling, and analysis.
- Nodes and Pods – Worker machines that deliver containerized applications.
- Kubernetes Services – Allow communication between different parts of an application, assuring seamless connectivity.
By mastering these elements, you can optimize cluster performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Practical Learning: Responsive Tutorials and Practical Experience
The theory about Kubernetes is okay. However, without experience, you are the same as a beginner. Platforms like Minikube, Kind, and Play with Kubernetes provide environments where you can test Kubernetes controls without setting up a full system. These tools help you investigate Kubernetes cluster setups, workload scaling, and troubleshooting.
For example, practicing Kubernetes deployment by launching containerized applications and automating rollouts ensures you’re prepared for production scenarios. Collaborative labs provide step-by-step exercises to strengthen learning, making it easier to apply Kubernetes in real-world settings.
Advanced Topics: Scaling Beyond the Basics
Once you've understood the basics, it's time to explore more complex topics:
- Multi-Cloud Deployments – Running Kubernetes across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud for dependability.
- Security Best Practices – Applying Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and network policies.
- Microservices Management – Using Kubernetes services to secure smooth communication between microservices.
Securing an AWS Root Account is an important best practice for professionals managing cloud security. Understanding these latest topics will also make you ready for large organization-level Kubernetes implementations and certifications like the AWS Certified Solutions Architect exam.
Real-World Applications of Kubernetes
Organizations worldwide use Kubernetes to streamline operations. Some key examples include:
- Scalable Web Applications – Companies deliver Kubernetes for high-traffic sites, managing loads more effectively.
- Big Data & AI Workloads – Kubernetes accelerates machine learning systems and large-scale data operation.
- Serverless & Hybrid Cloud Executions – Businesses compare AWS App Runner vs. ECS vs. Lambda to determine the best system for their needs.
By understanding these practical applications, you can make informed decisions when executing Kubernetes in your projects.
Conclusion:
Kubernetes (k8’s) is the next big wave in cloud computing, and it’s easy to see why as businesses migrate their infrastructure and architecture to reflect a cloud-native, data-driven era.A strong introduction to Kubernetes needs more than just theoretical knowledge—you need hands-on experience, architectural insights, and exposure to advanced concepts. Whether you're an aspiring cloud professional or an experienced DevOps engineer, mastering Kubernetes will open doors to high-paying roles. Ready to take the next step? Explore expert-led Kubernetes training at NovelVista and elevate your cloud career today!
Ready to Take Your Kubernetes Skills to the Next Level?
Master the art of container orchestration with the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) course.
👉 Enroll Now in CKA Certification Training
Author Details

Vaibhav Umarvaishya
Cloud Engineer | Solution Architect
As a Cloud Engineer and AWS Solutions Architect Associate at NovelVista, I specialized in designing and deploying scalable and fault-tolerant systems on AWS. My responsibilities included selecting suitable AWS services based on specific requirements, managing AWS costs, and implementing best practices for security. I also played a pivotal role in migrating complex applications to AWS and advising on architectural decisions to optimize cloud deployments.
Confused About Certification?
Get Free Consultation Call










